Recently here at OASIS, Head of Surgery and specialist in orthopedics, Dr. Harvey Zhou successfully completed minimally invasive surgery of a comminuted tibiofibular fracture with the help of an electromagnetic navigation system.
The patient was a 19-year-old man from France. He had been in a car accident causing him to sustain a comminuted fracture (break or splintering of the bone into more than two fragments). Due to the difficulty involved in treating such a fracture, the patient consulted many hospitals before finding himself at OASIS International Hospital. Dr. Zhou proposed a “closed reduction with intramedullary nail fixation under electromagnetic navigation system”. The surgery was completed successfully within one hour and the patient released from hospital after two days. At present, the patient is in good condition and recovering at home after surgery.
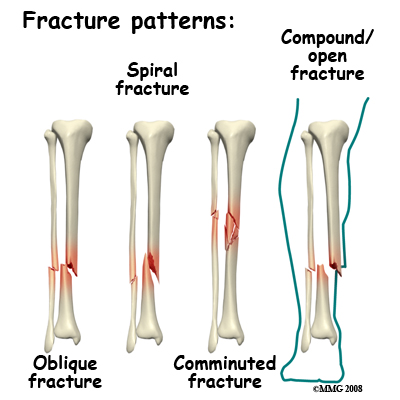
Treatment of tibiofibular fractures differ depending on the type of fracture, which include:
-Open reduction internal fixation (ORIF): This method can easily effect blood supply to the injured area and damage soft tissue. After surgery, there’s a possibility of nonunion of the fracture, which is a serious complication causing permanent failure to heal. This can occur if there is poor blood supply to the fractured area or infection occurs.
-Closed reduction and external fixator: This method is used as a last resort as this surgery is very troublesome for the patient. Patients will be inconvenienced when trying to move about, the risk of infection is higher and it requires a follow-up internal fixation surgery.
-Closed reduction and Intramedullary Nail Fixation: This blind surgery technique is performed under the guidance of X-ray or imaging. The technology is quite complex, the size of the rod to use in the surgery is not easy to choose and complications are quite common. Commonly it is difficult for the surgeon to lock the lock-pin on the distal of intramedullary nail during the procedure, which increases the operation time, leaving the patient under x-ray exposure for much longer.

The incision is quite small and not overly invasive
Dr. Zhou chose closed reduction with intramedullary nail fixation under electromagnetic navigation.
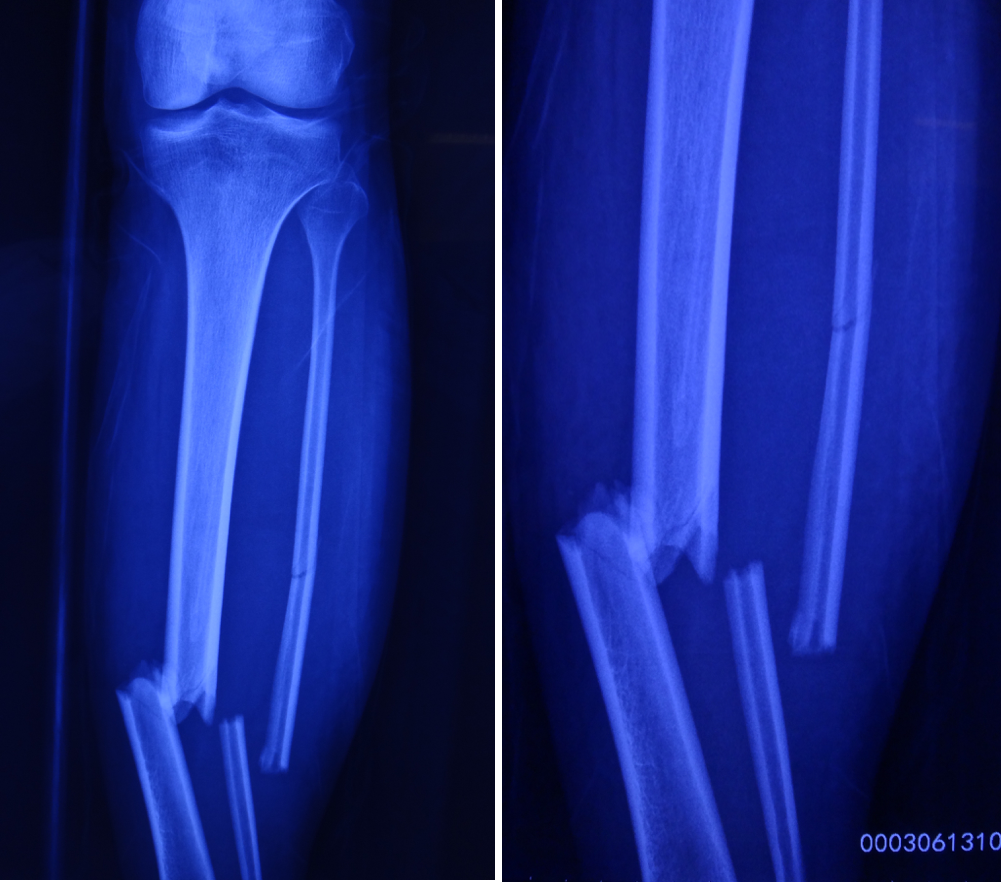
Advantages associated with this surgical method include:
-Minimally invasive: In a change to traditional open surgery methods, this method does not expose the fracture. A small incision is made for the insertion of the intramedullary nail into the medullary cavity. Under the guidance of electromagnetic navigation, the nail can be inserted into the cavity to the required depth of the fracture.
-Low chance of infection, faster recovery: Avoiding open surgery means less damage to the surrounding tissue and blood supply to the fracture. Chance of infection is also greatly reduced.
-Shortened surgical time: With the use of electromagnetic navigation, the surgery can now be performed with live visual footage as opposed to traditional blind methods, requiring a dynamic reference framework to work from. This allows the surgical method to be more accurate, reduce surgical trauma, post-surgical complications as well as the surgical time.
-Less radiation exposure: In traditional blind methods, the fixation of the rod requires taking multiple images using the C-arm imaging machine. Repeated imaging throughout the surgery exposes both the patient and physician to much radiation. Using electromagnetic navigation, this allows for real-time accurate visualization of the area, reducing the radiation exposure during surgery.
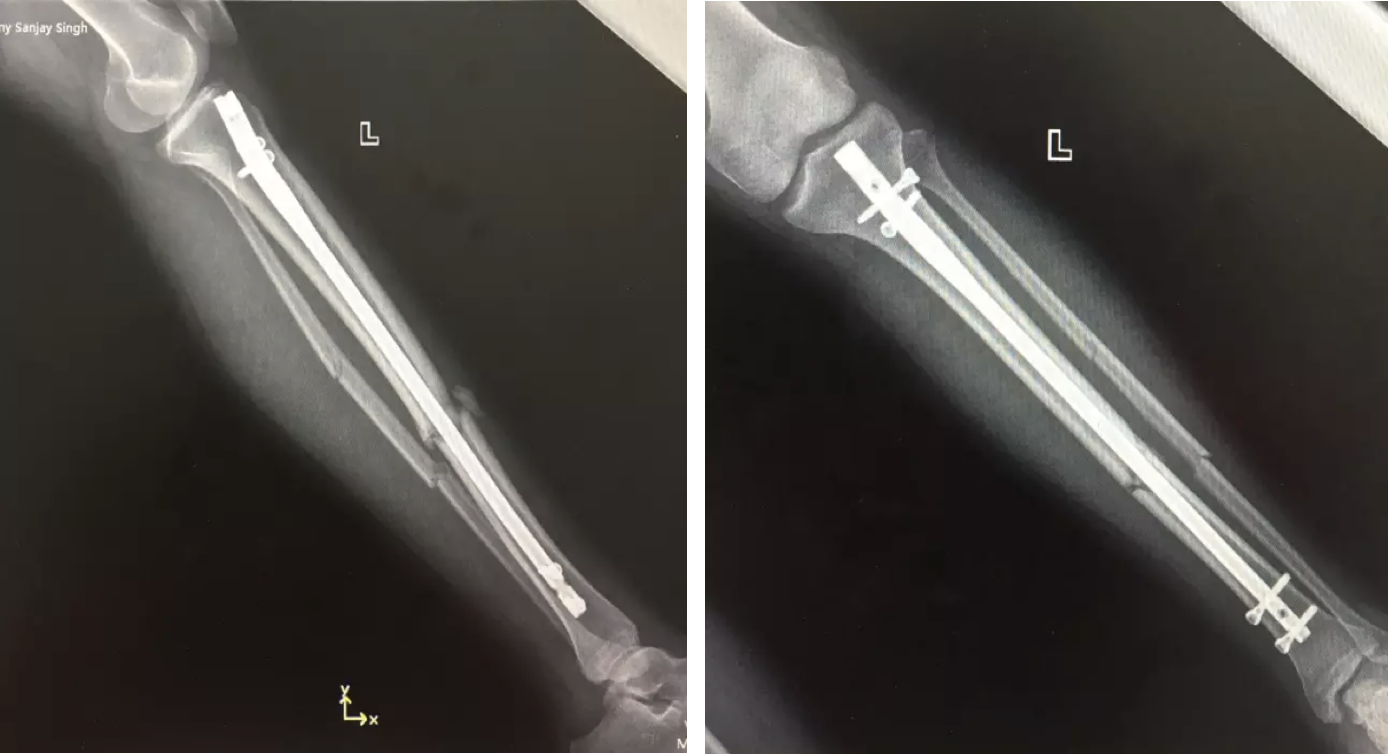
At present, there are only a small number of hospitals in Beijing that possess electromagnetic navigation system technology. OASIS International Hospital possesses one of the leading international navigation systems, bringing its minimally invasive surgical methods to new heights. Dr. Zhou explains: “Having an electromagnetic surgical navigation system for the treatment of long bone fractures not only confirms the international trend for medical precision, moreover it reduces surgical trauma to the patient, which improves the safety of this surgery for patients.

Dr. Harvey Zhou
Head of Surgery and Orthopedic Specialist
Nationality: China
Language: Chinese, English
Dr. Zhou obtained his MD in Orthopedics from Peking University Third Hospital and completed his Postdoctoral in Orthopedics in the PLA General Hospital. Dr. Zhou has almost 30 years’ experience in Orthopedics, completing over 9000 orthopedic surgeries. During this time, Dr. Zhou also underwent 8 months of clinical training in Microsurgery and Hand surgery. He successively studied at: Joint Surgery at Hong Kong Queen Mary Hospital, Joint Surgery and Spinal Surgery at The University of California, San Francisco and Spinal Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital. Dr. Zhou was once Chairman of Orthopedics and Head of Technology at Beijing Yanhua Hospital. He is also Chair of the Beijing Fangshan District Orthopedic Committee. Dr. Zhou has published over 10 papers in journals, such as, the American journal – “Spine” and the Oxford journal – “Rheumatology”.
Specialized Areas:
Dr. Zhou specializes in various treatments of acute and chronic sports injuries; standard and minimally invasive surgical techniques to treat a variety of degenerative spinal diseases, idiopathic scoliosis, spinal tuberculosis and tumors; kyphoplasty for vertebral fractures caused by osteoporosis; artificial hip and knee replacement and revision surgery; artificial shoulder joint and metacarpophalangeal joint replacement surgery; the use of spinal injections to diagnosis and treat neck and shoulder pain, lower back pain and sciatica. Dr. Zhou is also proficient in 0.3mm microvascular anastomosis, as well as, microsurgical reconstruction and repair.
This blog is sponsored by OASIS



